If you’re like most people, you probably don’t know a lot about CHQ wire. That’s why we’ve put together this essential guide to help you understand everything you need to know about CHQ wire. We’ll cover everything from what it is and how it’s used, to the benefits and drawbacks of using CHQ wire. By the end of this guide, you should have a much better understanding of this popular wiring method. So let’s get started!
What is CHQ wire?
The term “cold heading quality” refers to steel wire that is created by drawing and annealing wire rods. HRPPD Process, DAPPD Process, and SAPPD Process are the three primary cold heading processes – manufacturing methods used to make CHQ Wires.
What is Chemical Composition of CHQ Wire?
CHQ wires contain carbon and manganese in amounts that provide good corrosion resistance. The amount of chromium varies depending on the grade.
CHQ wire has chemical composition of 0.2% to 1.0% carbon, 0.5% to 2.0% manganese, 0.3% to 0.8% silicon, 0.05% to 0.15% chromium, 0.1% to 0.4% nickel, 0.001% to 0.03% copper, and balanced iron.
How is CHQ Wire Manufactured?
CHQ Wire Manufacturing Process
Quality raw material i.e. quality wire rods is essential for making good quality chq wires. Also coating on wire rods should be uniform and free from defects. Finished product should have high tensile strength and ductility. It should also have good corrosion resistance. Heat Treatment process is very important for producing high-quality chq wire. High temperature heat treatment can improve the physical properties of chq wire and improved tool life.
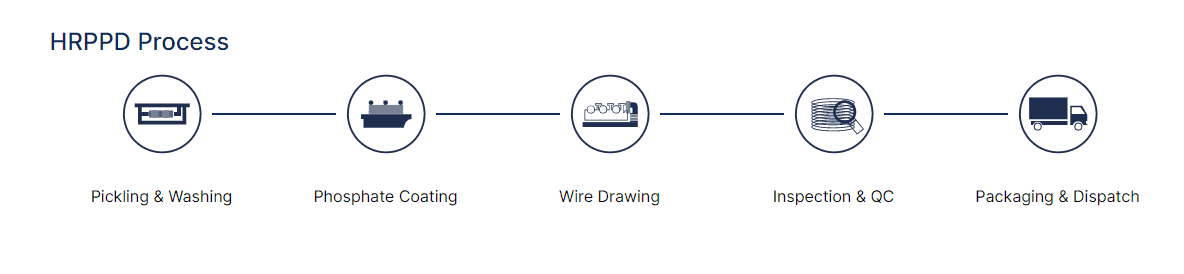
HRPPD Process

The HRPPD process is the most common method and involves five stages: pickling and washing, phosphate coating, wire drawing, inspection and QC, and packaging and dispatch. The key difference between HRPPD and other processes is that the wire does not undergo spheroidized annealing.
Phosphate coating is applied during the phosphate coating stage. This layer of coating helps to protect the wire from corrosion and extends its life. The wire is then drawn through a series of dies to reduce its diameter.
Inspection and QC are carried out during the inspection and QC stage to ensure the wire meets the required standards. The wire is then packaged and dispatched for use.
Stages of HRPPD Process
- Phosphate Coating
- Wire Drawing
- Inspection & QC
- Packaging & Dispatch
SAPPD Process

Under the SAPPD process, wire under spheroidized annealing. This process eliminates decarburization and provides improved tolerances when cold drawing from appropriate input sizes. It also helps to avoid ovality by providing tighter tolerances in drawing from proper input sizes and uniform grain size.
Stages of SAPPD Process
- Spheroidized Annealing
- Pickling, Washing & Coating
- Final Wire Drawing
- Inspection & QC
- Packaging & Dispatch
DAPPD Process

The DAPPD process is similar to the SAPPD process. However, the wire is pickled, washed, and coated twice. It also goes through an intermediate drawing procedure before being spherodized annealed. Nitrogen atmosphere is preferred at this stage.
Stages of DAPPD Process
- Pickling, Washing & Coating
- Intermediate Drawing
- Spheroidized Annealing
- Pickling, Washing & Coating
- Wire Drawing
- Inspection & QC
- Packaging & Dispatch
What are the main benefits of CHQ Wires?
- Improved tolerances when drawing from appropriate input sizes
- Eliminates decarburization
- Provides tighter tolerances in drawing from proper input sizes
- Reduced ovality by providing tighter tolerances in drawing from proper input sizes
- Higher strength-to-weight ratio than other types of steel wire
- Enhanced Fatigue Strength
- CHQ wires have higher yield strengths compared with conventional grades of steel wire. These high yield strengths make them more resistant to fatigue damage. In addition, they exhibit superior fatigue resistance compared with other types of steel wire.
How is CHQ Wire Graded?

CHQ Wire is graded according to ASTM A53/A543 (Grade 1) or ASTM A53/C591 (Grade 2). Grade 1 has a minimum tensile strength of 895 MPa and Grade 2 has a minimum tensile stress of 930 MPa. Grade depends on the size of wire used. For example, Grade 1 wire can be used up to 0.6mm whereas Grade 2 wire can be used up till 0.8mm.
What is Fatigue Strength of CHQ wire?
Fatigue strength of CHQ wire is measured in terms of yield strength (YS) and ultimate tensile strength (UTS). Yield strength is the maximum stress at which the wire will break when stretched under constant load. Ultimate tensile strength is the highest stress at which the wire can sustain without breaking. Fatigue strength is the average life of the wire before it breaks. Fatigue strength is calculated by dividing the total number of cycles by the average cycle length. Fatigue resistance of CHQ wire is defined as the time period after which fatigue failure occurs.
What Are The Main Cold Heading Applications?
The most common major applications of cold heading wire is in fasteners such as screws, nails, and bolts. It is also used in a range of other major applications like industrial applications, including automotive parts, medical implants, aerospace industry, construction industry, and hardware. Surface quality is critical in these applications because they will be exposed to harsh environments. For this reason, it is important to choose the right type of wire with high tensile strength and smooth surface.
Critical Fasteners
CHQ wires finds its usage in various industries like Automotive Industry, Engineering Industries, Appliances & Cold forging and fastener applications (like wire for nut bolts).
In general, thread cutting or hot working has been used to create fasteners. However, using the cold working technique to increase production and keep costs low is increasingly popular in fastener uses.
The benefits of this method include excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy in fasteners. In regions with dissimilar deformation ratios, the cold heading procedure produces significant hardness divergences.
As a result, to minimize scattering of the fastener qualities, an appropriate balance & mechanical characteristics of the raw material must be maintained.
Cold Forged Parts
CHQ wires are widely used in the automotive industry for cold forged parts. This includes engine components, transmission components, suspension components, and interior components. These parts require high-quality materials that provide good surface finish and dimensional accuracy. They should also have sufficient strength to withstand severe operating conditions.
These parts are subjected to extreme temperatures during operation, so the properties of the steel need to remain stable over long periods of time. CHQ wires are ideal for use in these types of applications because they are strong, durable, and easy to work.
Armature Shafts

Another common application for CHQ wire is in armature shafts. Armature shafts are an important component of electric motors and generators, and they need to be able to withstand significant amounts of torque.
Ball & Roller Bearing

CHQ wire is also used in ball and roller bearings. Ball and roller bearings are essential for transmitting power and motion in a wide range of industrial applications, and they need to be able to withstand significant amounts of torque.
Ball Joint Stud

Ball joint studs are commonly made from cold heading quality wire. They are used to join two metal parts together and are available in a variety of sizes and styles. They are a popular choice for use in automotive and engineering applications.
Chain Pin

Chain pins are made from cold heading quality wire and are used to join together the links in a chain. They are available in a variety of sizes, depending on the application. Chain pins are commonly used in automotive and engineering applications.
Cylinder Head Bolt

The connecting components between the engine block, cylinder head gasket, and cylinder head are called the Cylinder Head Bolt. It’s mostly composed of Stainless Steel and Carbon Steel. The head bolt is usually a hexagonal shape, and it screws into the engine block.
Drill Bit Pieces

Drill bit pieces are used to create a hole in a surface. They are made from cold heading quality wire to ensure that they have the strength and durability needed for these applications.
Screw

A screw is a fastener that is used to join two pieces of metal together. It is made from cold heading quality wire to ensure that it has the strength and durability needed for these applications. Screws are commonly used in automotive and engineering applications.
Nuts & Bolts

Nuts and bolts are made from CHQ wires . These are typically made from cold heading quality steel and are used in many different types of applications.
Tire Spoke

A tire spoke is the part of a bicycle wheel that connects to the hub and holds the tire in place. They are made from either steel or aluminum, depending on the frame design. The spokes are usually arranged so that they cross at right angles, forming a diamond pattern.
Tubular Rivets

Tubular rivets are used to connect two surfaces together. Tubular rivets are often made from stainless steel and can be used in a variety of industries. They are especially useful when making connections where weight matters, such as aircraft fuselages.
So, there you have it – our essential CHQ wire guide. We hope this helps demystify some of the questions you may have about these unique wires and their capabilities. If you’re looking to buy CHQ wires, we invite you to browse our selection and contact us if you have any questions. Thanks for reading!
